Introduction
Last week we submitted out Go-to-Manufacturing Report. In this report we dive into detailed analyses of out injection molded parts using Autodesk Moldflow simulation. Detailed drawings of necessary tooling are included. We also take a first pass at estimating several operational parameters necessary for producing yo-yos at a scale of 1 million per year. Finally, a simplifies schematic of a factory layout in included to visualize the space requirements for this operation.You should be able to find the complete GTM Report here.
Yo-Yo Design Overview
The final design of our yo-yo includes a plastic cup exterior, filled with swirling liquid and garnished with a lime, designed to mimic a Cosmopolitan cocktail.
The yo-yo features three injection molded pieces and one thermoformed piece, as well as two press-fits. The exploded view and section view below label the components and how they interact with each other.
Moldflow Analysis
We used Moldflow to calculate the process and geometric parameters that would allow us to achieve the optimal combination of rate, cost, and quality for our injection molded parts. All analysis was conducted assuming the use of polypropylene material with a 392° F injection temperature, 68° F mold temperature, and a maximum injection pressure of 37000 psi, corresponding to the capabilities of the BOY-22A. Some examples of our results are shown below.
Design Changes
Based on Moldflow analysis as well as mold design considerations, we modified the injection molded part geometries to achieve the highest chance of producing high-quality parts which will fit together properly. Our changes are summarized as follows:General
- Scaled up parts based on estimated shrinkage when designing molds
- Added tolerances for interference fits based on part size and capability of milling machines
- Left tolerances low wherever possible (aesthetic parameters)
Lime
- Hollowed out inside of press fit to promote more uniform cooling
Liquid
- Added draft angles on inside of liquid bottom
- Considered alternative ripple designs for liquid top but kept original design-based mold-making feasibility
- Added filets to sharp corners on the liquid top to comply with smallest tool diameter
- Changed thicknesses on certain areas to comply with smallest tool diameter
Material Selection
A summary of our materials choices is shown below.
String
50/50 blend of cotton and polyester for high friction, durability, and comfortable feel.
Glass
HDPE was selected because of its very high strength and clear glass-like finish. PETG was considered but is brittle especially at thinned locations such as the one in the yo-yo.
Liquid Bottom/Top/Lime
The injection molded parts will be made from polypropylene. Polypropylene is inexpensive and resistant to impact forces. Additionally, it works well with snap fitting such as in snap-over lids. Other materials were considered such as ABS, polycarbonate, ABS/PC, polyamides, acrylic and polyoxymethylene.
Bill of Materials
Tooling
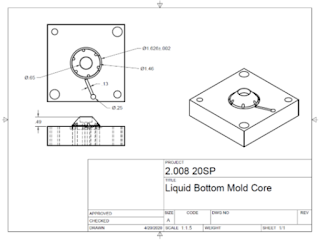
We created drawings for the tooling used to create our yo-yos. Each tooling is designed to be manufactured from aluminum stock on the TRAK milling machine. The tooling includes the Glass Die, Liquid Bottom Mold Core, Liquid Bottom Mold Cavity, Liquid Cap Mold Core, Liquid Cap Mold Cavity, Lime Mold Core, and Lime Mold Cavity. The Glass Die is the tooling for our thermoformed part, and the remaining molds are for injection molded parts of our yo-yos.
For the lime mold, we needed to create a custom tool based of commercially available end mills. The narrow slots require low cutting forces and a long cycle time to ensure good finishing. We went with a 0.020" flat end mill which had a length of 0.75". Though this tool is very long, we minimized deflection by reduction the amount of material removed with each revolution. The finishing passes are done with a separate tool of equivalent size to ensure high quality surfaces.
Some examples of tooling drawing are shown below.
Production
The following table shows several of our underlying assumptions and resulting operational requirements in order to fill a production demand of 1 million yo-yos per year.
Molding Cycle Times
A key driving factor in how our production rate is the cycle time of each injection molding operation. The following table and donut charts show cycle times for each injection molded part and their respective breakdowns.
Injection Molding Cost Estimates
Detailed cost estimates are listed in the table below. They are organized by material cost, mold cost, molding cost, total cost, and total cost per shot.
Thermoforming Cost Estimates
Industry experts advised our team to contract out the thermoforming process since we could realistically achieve production rates an order of magnitude greater than what we can achieve with our injection molding process. To avoid investing in equipment that will run for one or two months a year and remain idle for the rest of the time, we will be contracting out the thermoforming production of our plastic glass parts.
Innovative Plastics quoted us a price of $50,000 to deliver 2 million plastic glass pieces made of 0.030” HDPE. They told us that they could fill our order in two months.
Total Costs
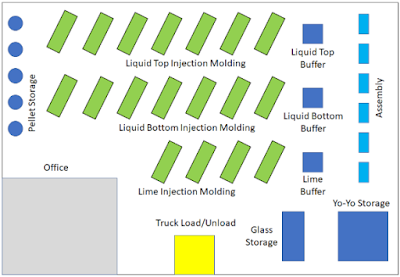
Factory Layout
Based on our calculations, we can up with a simplified schematic of what a factory floorplan might look like.













No comments:
Post a Comment